Permissions
DbGate’s permissions use two dimensions:
-
Source of permissions (who sets them) Permissions cascade from broad to specific. More specific settings override more general ones:
- Predefined permission sets
- Predefined roles (superadmin, logged user, anonymous)
- Custom roles
- Individual user
-
Object scope Permissions can target specific databases and tables/objects. See Database permissions and Table permissions.
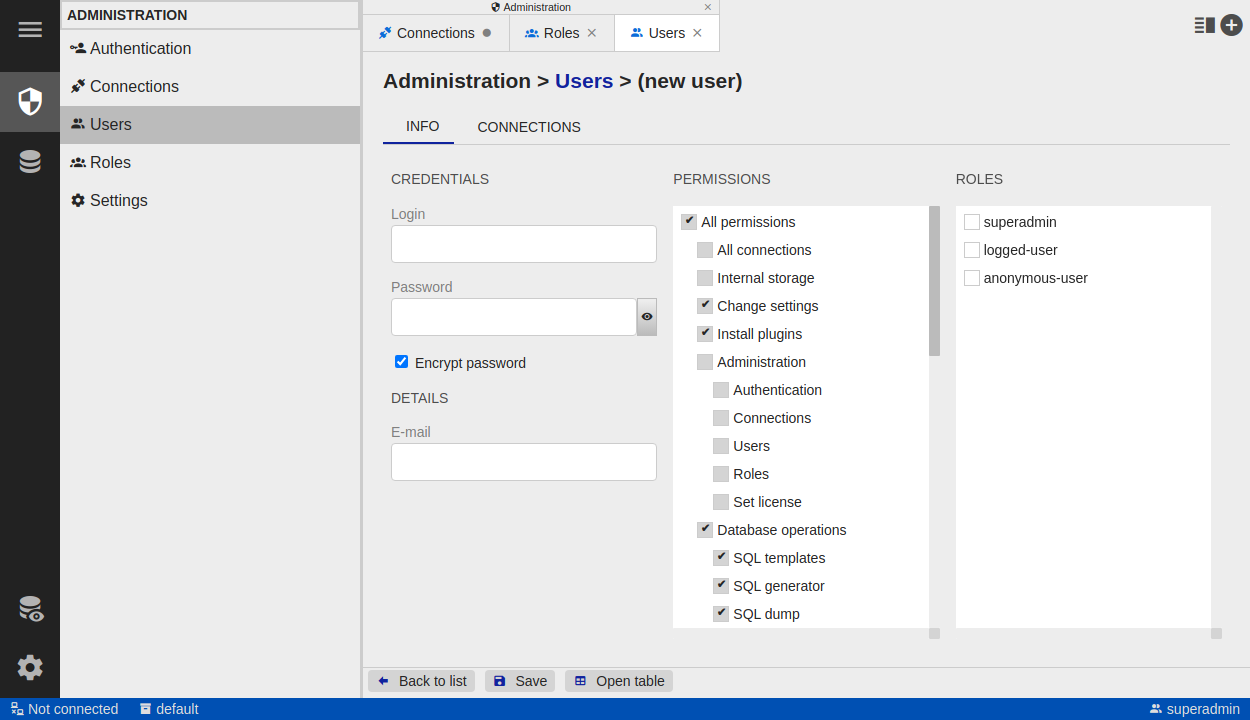
Basic Permissions
Configure global/basic permissions in the permission tree in User detail or Role detail.
- A greyed checkbox means the permission is inherited (e.g., from a role or a predefined permission set), not set directly on that user/role.
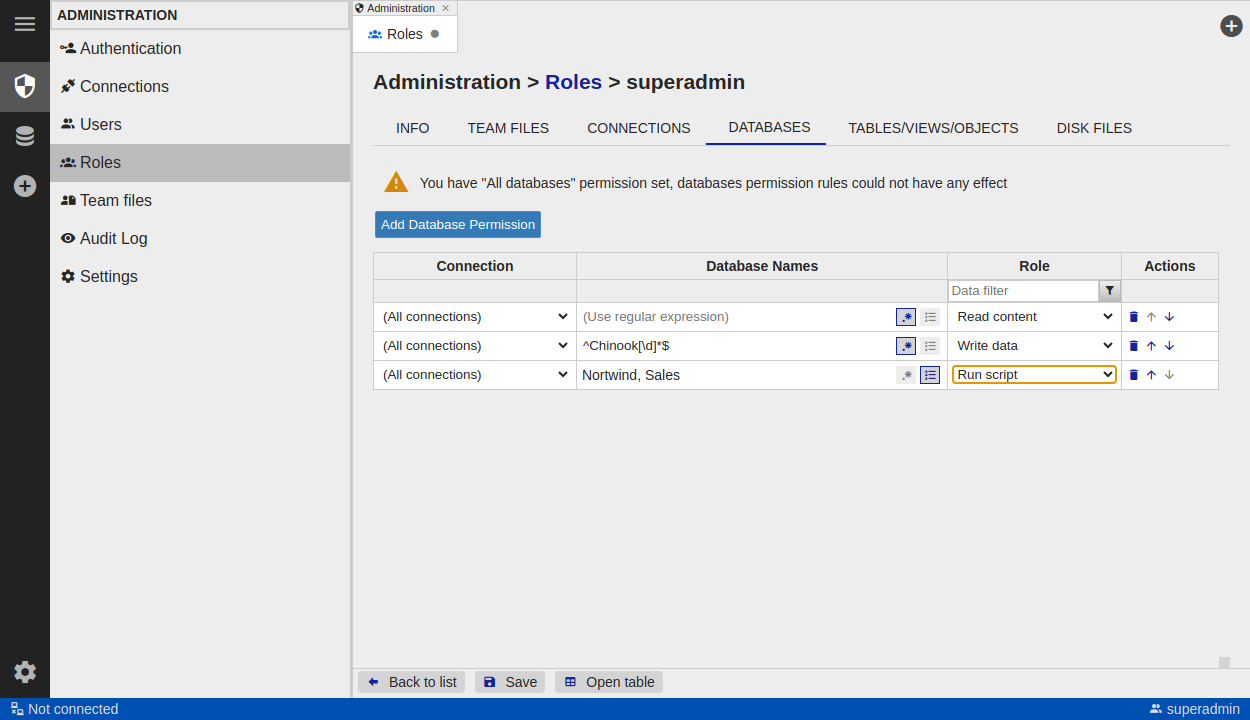
Database Permissions
Set database-level permissions on the Databases tab (in both Role detail and User detail).
Important: Database rules are applied only if the “All databases” permission is unchecked in the basic permissions.
- Each row in the rules table grants or denies access to databases that match the row’s filters.
- Rule order matters: rules lower in the list override rules above them.
Columns
- Connection – which connection the rule applies to.
- Database names – databases to match (list of names or a regular expression).
- Role (access level)
- View – can see the database, but not its tables/views/etc.
- Read content – read-only access to database content.
- Write data – can modify table data.
- Run script – can run any SQL script; can create/drop/alter objects.
- Deny – blocks access to the database.
Table Permissions
Set table/object-level permissions on the Tables / Views / Objects tab (in Role detail and User detail).
Important: Table/object rules are applied only if the “All tables/views/objects” permission is unchecked in the basic permissions.
- Each row defines access to tables/objects that match the filters.
- Rule order matters: rules lower in the list override rules above them.
- By default, table permissions are inherited from the database permission.
Columns
- Connection – which connection the rule applies to.
- Database names – databases to match (list or regular expression).
- Schema names – schemas to match (list or regular expression).
- Table names – object names to match (table/view/procedure/trigger) as a list or regular expression.
- Scope – which object types the rule covers (tables, views, procedures, triggers, …).
- Role (access level)
- Read – can read table data.
- Update only – can update rows; insert and delete are not allowed.
- Create, update, delete - can edit rows without restrictions
- Run script – can run a script that touches this object.
Note: If you don’t have “Run script” at the database level, you cannot use it at the table level.
- Deny – blocks access to the object.